The Ultimate Guide to Rainwater Gutter Installation in Easy Steps
Rainwater gutter installation is essential for safeguarding your home from water damage. This guide covers every step: planning, measuring, cutting, and installing gutters and downspouts. Follow along to ensure your system works effectively and keeps your home dry.
Key Takeaways
-
Installing rain gutters is essential for protecting a home’s foundation and preventing costly water damage, erosion, and mold growth.
-
Thorough planning, accurate measurements, and the right materials are critical for a successful gutter installation, which includes assessing roof pitch and strategically placing downspouts.
-
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and inspecting gutters and downspouts, is crucial for ensuring long-term performance and preventing clogs that can lead to structural damage.
Why Installing Rain Gutters is Crucial
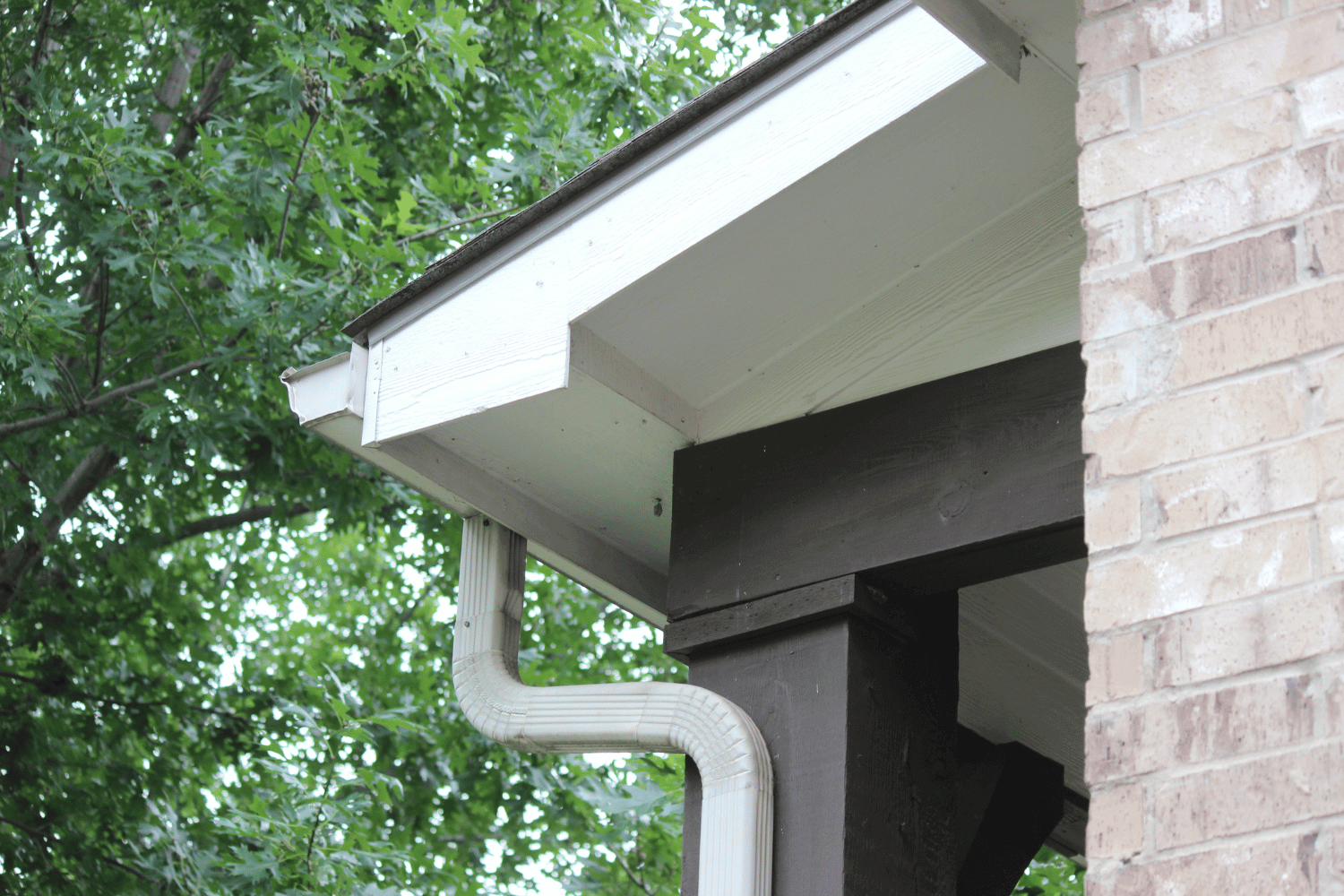
Rain gutters are the unsung heroes of home maintenance, playing a pivotal role in diverting and carrying rainwater away from your home’s foundation, thus protecting its overall structural integrity. Without a well-installed gutter system, homes are vulnerable to severe water damage, including roof leaks and erosion, which can lead to costly repairs.
Moreover, installing gutters helps preserve the condition of your siding and roof materials by directing rainwater away, thus preventing the degradation of these essential components. Improper water runoff can lead to mold growth, which not only causes structural damage but also poses health risks to residents.
Basement flooding is another significant concern that can be avoided with a proper gutter system. When rainwater is not diverted effectively, it can seep into the basement, leading to extensive water damage and creating a damp environment that attracts pests. Additionally, without gutters, the garden areas around your home can suffer from excess moisture, harming plants and creating pollution.
Rain gutters represent a small investment that can prevent substantial, costly damage, keeping your home safe, dry, and structurally sound. To protect your home effectively, it is essential to install rain gutters and ensure that the rain gutter system is functioning properly.
Planning Your Rainwater Gutter Installation Project
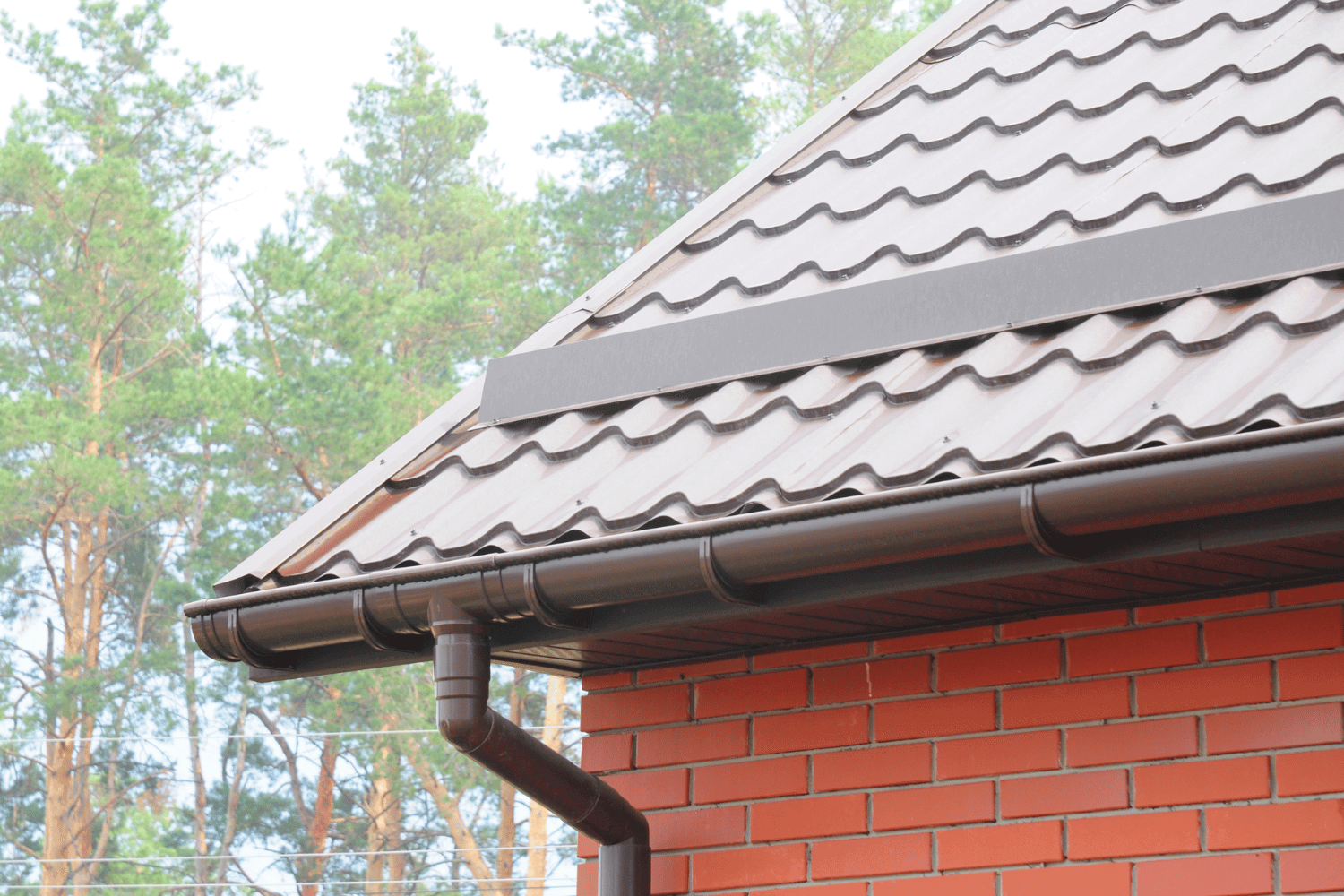

Thorough planning is necessary before installing rain gutters. Start by assessing your house’s structure and any existing components to ensure compatibility with the new gutter system. Visualize the layout by drawing a plan that identifies the lengths needed and the overall configuration of the gutters. This step helps in determining precise measurements and placement of the gutters, preventing overflow and foundation damage.
Next, calculate the roof’s pitch by measuring both horizontally and vertically to determine the slope. An appropriate slope ensures efficient water flow away from the foundation, preventing water-related problems. Strategically place downspouts to facilitate efficient drainage, keeping in mind that a downspout is generally needed for every 20 feet of gutter length.
Lastly, budget for additional materials beyond the gutters, such as brackets, downspouts, and potential repairs. Such comprehensive planning lays the groundwork for a smooth and successful gutter installation.
Essential Tools and Materials for Gutter Installation
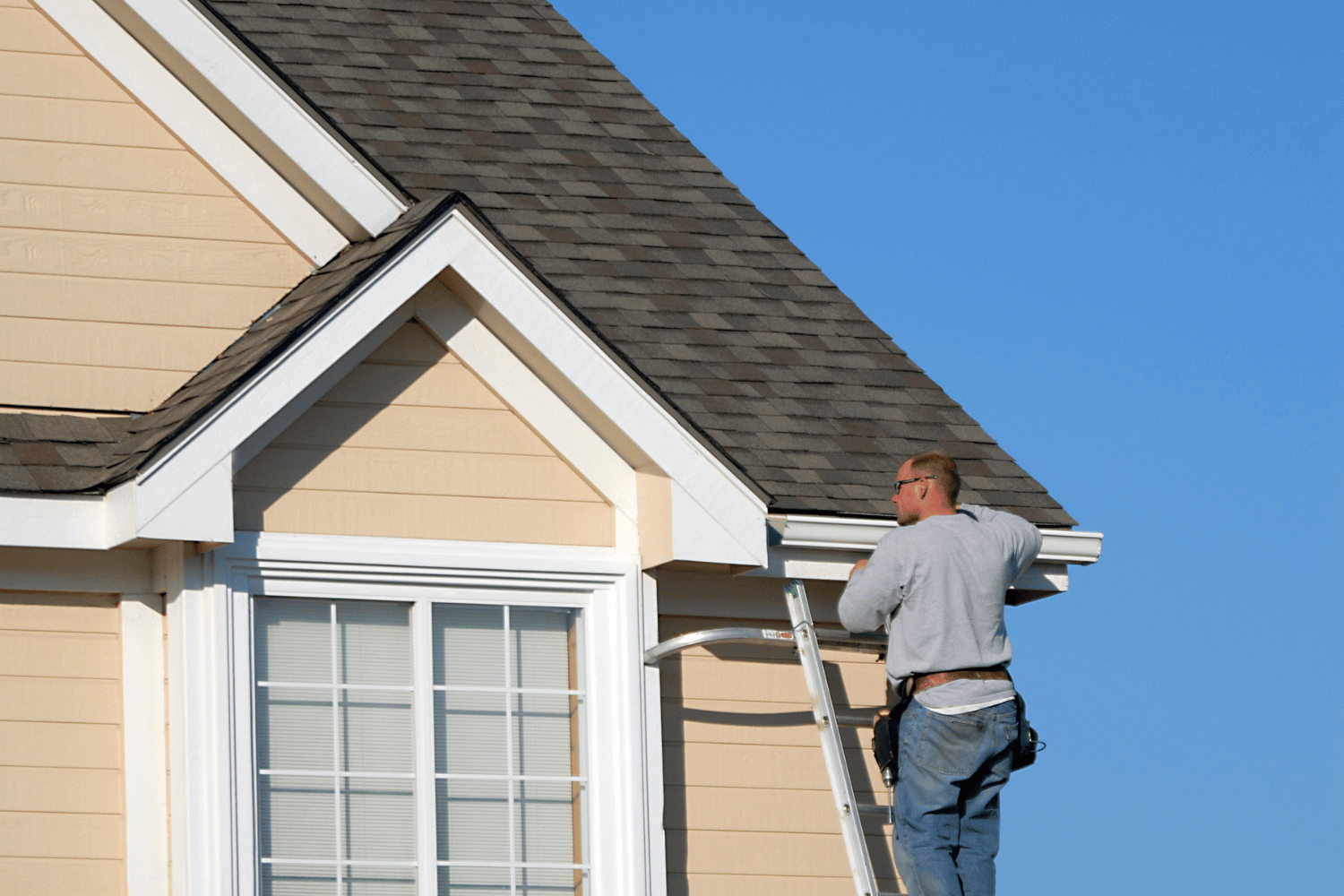

Installing gutters effectively requires a range of essential tools and gutter material. Aluminum gutters, gutter sealant, and stainless steel screws are fundamental components of a quality gutter installation. Aluminum gutters are particularly popular due to their durability and resistance to rust.
Before:
The necessary tools for the job are equally important. You’ll need tin snips and a hacksaw for cutting the gutters to the desired lengths. A cordless drill and a hex head driver are also necessary for securing the gutters to the fascia board. Additionally, a drill with a 4-inch hole saw bit is recommended for making downspout holes in the gutters.
After:
The necessary tools for the job are equally important. You’ll need:
-
Tin snips and a hacksaw for cutting the gutters to the desired lengths
-
A cordless drill and a hex head driver for securing the gutters to the fascia board
-
A drill with a 4-inch hole saw bit for making downspout holes in the gutters
Don’t forget the additional components like gutter fascia, which should be on hand for installation. Having the proper tools and materials equips you to tackle your gutter installation project efficiently.
Measuring and Marking for Precision
Accuracy is crucial when installing rain gutters. Inaccurate measurements can lead to water pooling in the wrong places or an inefficient use of materials. Start by marking the highest and lowest points of the gutter run to establish the necessary slope for effective water flow. Usually, the pitch should be set at 1/2 inch for every 10 feet toward the downspout to ensure proper drainage.
Using a chalk line helps maintain the correct level and alignment of the gutters. Snap a chalk line between the highest and lowest points to guide your installation.
Tools such as a tape measure and RoofScope or GutterScope help in taking exact measurements, ensuring accurate installation and proper functioning of your gutters.
Cutting and Preparing Gutter Sections
Once you’ve measured, it’s time to cut and prepare the gutter sections. Saw the sections to the correct length, accounting for any corners or turns where elbow joints are needed. Use tin snips to cut outlet holes for downspouts and smooth out any sharp edges with a file to ensure seamless connections.
Pre-drilling holes for the gutter end caps and applying gutter sealant at the joints ensures leak-free connections. Properly preparing gutter sections is essential for a tight fit and effective water flow.
Installing Fascia Brackets and Hangers
Installing fascia brackets and hangers is a vital step in the gutter installation process. Begin by measuring the gutter length and marking hanger positions for even spacing. Use a ladder to safely access the roofline and drive spikes into the fascia board for secure attachment when using spikes and ferrules.
Ensure the screws used for attaching hangers are long enough to securely penetrate both the gutter and the fascia. Avoid positioning hangers directly over downspouts to prevent water flow issues. Hidden hangers, which are not visible from the ground, provide a neat appearance and enhance the overall aesthetics of the gutter system.
For added security, install gutter hangers through the fascia board into the rafter ends whenever possible. This method ensures a robust attachment, capable of supporting the weight of the gutters and the water they will channel.
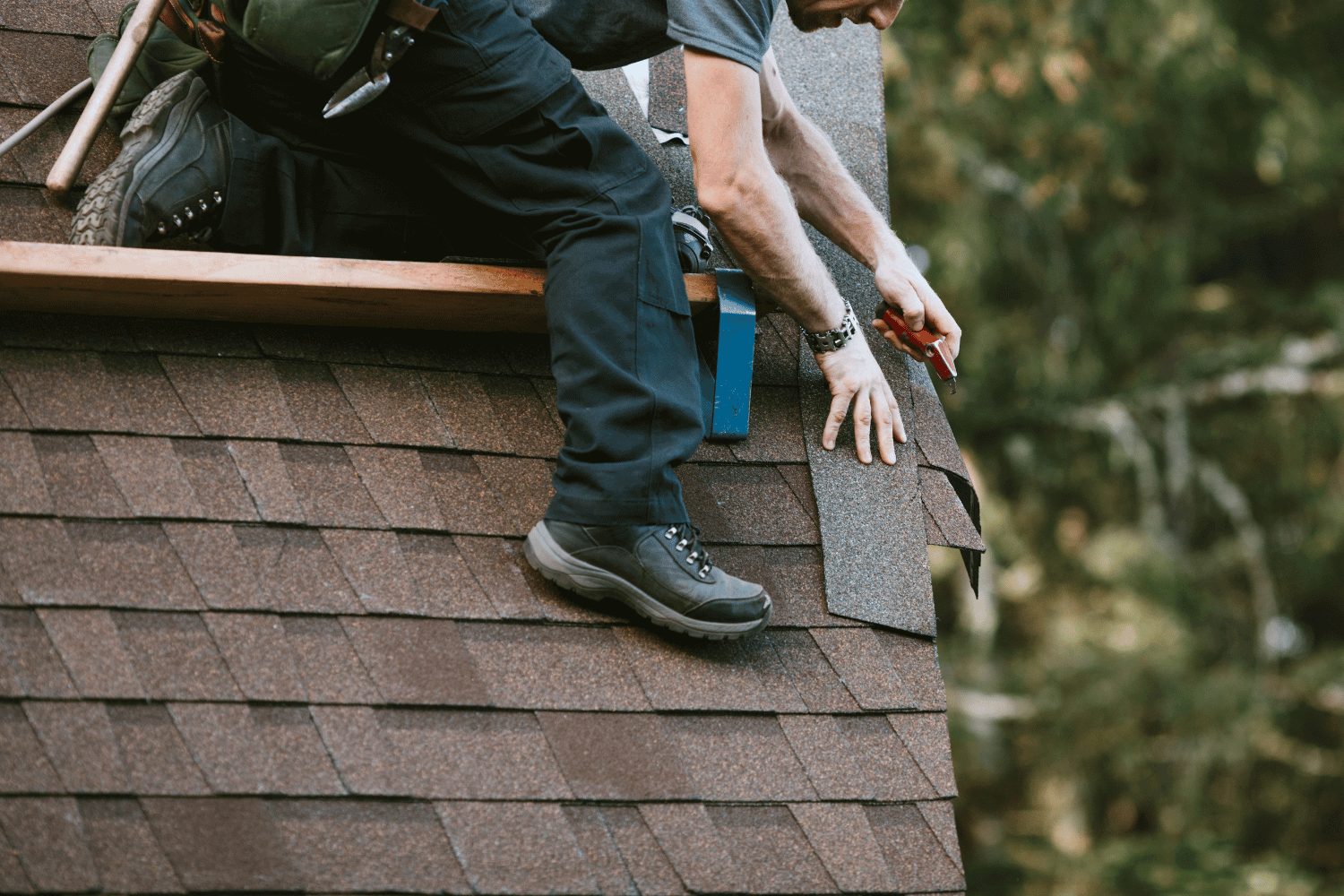
Attaching the Gutter Sections
Now that the brackets and hangers are installed, the next step is to attach the gutter sections. Continue with this part of the setup. Begin at the highest point of the slope, positioning the sections in sequence near the installation site. Secure the sections using screws or gutter spikes, ensuring a sturdy connection.
For corners, use connectors or strips of metal to link two gutters together. Hook the back side of the strip miter through the rear edge and secure it with screws to ensure a tight fit. Brackets should be mounted every 18 to 24 inches to provide adequate support for the gutter runs.
Ensure that the installed gutters slope away from the downspout location to facilitate proper water flow and prevent pooling.
Sealing Joints and Connections
To prevent leaky gutters, sealing joints and connections is crucial. Apply gutter sealant along any seams to ensure that the gutters are watertight. This step is essential for maintaining the integrity of the gutter system and preventing costly repairs.
Apply sealant to all holes and elbows connecting gutter materials. Press the components tightly together after applying the caulk to ensure a secure, leak-free connection.
Installing Downspouts and Ensuring Proper Drainage
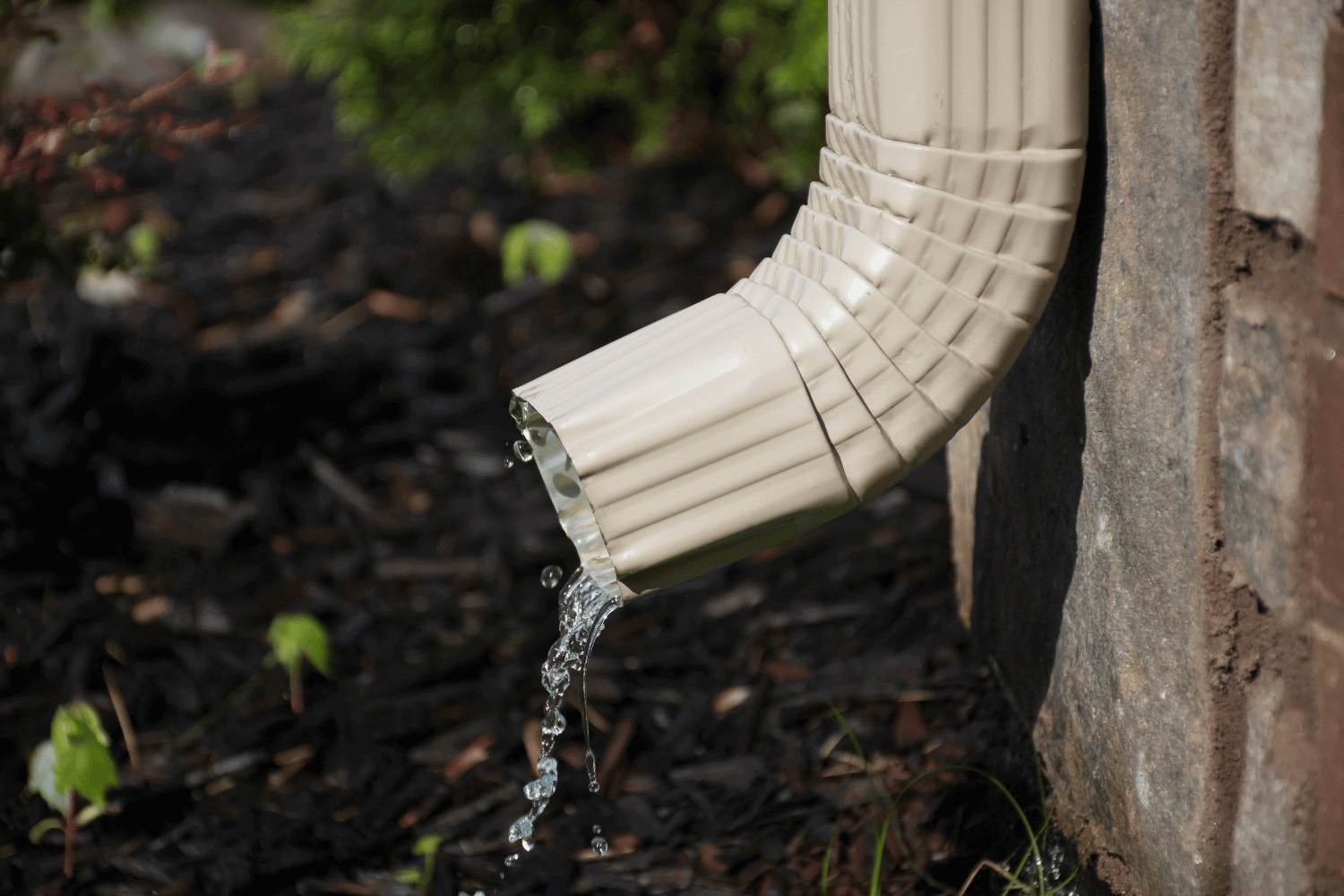

Correct downspout installation is vital for effective drainage. Determine the number and placement of downspouts to prevent water pooling around the foundation. Downspouts are typically installed at the ends of the gutter system. They can also be positioned at the corners.
Use brackets to secure the downspouts properly, attaching U-shaped elbow brackets to connect the downspout to the house corners. Downspout extensions can guide water further away from the foundation, reducing the risk of basement flooding.
For optimal performance, seal gutter seams on a warm, dry day and clean old caulk and debris before applying new sealant. Press the components tightly together after applying caulk to ensure a secure connection.
Adding Gutter Guards for Maintenance-Free Gutters

Gutter guards are an excellent addition to any gutter system, preventing debris buildup and reducing the frequency of gutter cleanings. Installing gutter guards helps keep the inside of the gutters clean, preventing water damage and ensuring proper flow.
Micromesh gutter guards are highly recommended for protecting rain gutters. LeafFilter gutter guards, for example, offer a clog-free guarantee, significantly reducing the need for regular cleaning.
Testing Your Installed Gutter System
After installation, testing the gutter system ensures it functions correctly. Run water through the system to check for leaks and observe water flow. This test helps identify any pooling or improper drainage issues needing attention.
Perform visual inspections to locate any visible damage such as cracks or sagging in the gutters. Promptly addressing these issues will ensure the longevity and effectiveness of your gutter system.
Tips for Maintaining Your Rain Gutters
Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity and performance of your rain gutters. Regular maintenance includes gutter cleaning and downspouts at least twice yearly to prevent clogs and ensure proper function. This practice helps avoid common issues such as clogs and leaks in the gutter system.
Using gutter guards minimizes the risks associated with cleaning gutters, reducing the time spent on ladders and enhancing safety. Gutter guards also lower the fire hazard risk by preventing debris accumulation that can catch fire.
Regularly check for signs of rust, corrosion, or sagging in your gutters. Inspect downspouts regularly for blockages to prevent overflow and subsequent damage.
Summary
Installing rain gutters is a critical task that protects your home from water damage and maintains its structural integrity. By following this guide, you’ve learned the step-by-step process of planning, installing, and maintaining a reliable gutter system. With proper tools, careful measurements, and regular maintenance, your gutters will efficiently divert rainwater away from your home, ensuring it remains safe and dry. Take action today and safeguard your home with a well-installed gutter system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do most houses in Florida not have gutters?
Most houses in Florida do not have gutters because they can trap debris, leading to clogs and potential roof damage, while the state’s wet climate and heavy rains make maintenance challenging. Consequently, many homeowners opt for alternatives to reduce upkeep.
Why is it important to install rain gutters?
Installing rain gutters is essential to protect your home’s foundation by redirecting rainwater away, which helps prevent structural damage, mold growth, and flooding. This proactive measure safeguards both your property and your investment.
What tools and materials are essential for gutter installation?
For gutter installation, essential materials are aluminum gutters, gutter sealant, and stainless steel screws, while necessary tools include tin snips, a hacksaw, a cordless drill, and a hex head driver. Ensuring you have these items will facilitate a smooth installation process.
How should I measure and mark for gutter installation?
To accurately install gutters, measure the highest and lowest points along the run, then snap a chalk line to establish a slope of 1/2 inch for every 10 feet toward the downspout. This ensures proper drainage and functionality.
What are the benefits of installing gutter guards?
Installing gutter guards effectively prevents debris buildup and reduces the need for frequent cleanings, ensuring proper water flow. This not only enhances safety by minimizing cleaning risks but also mitigates fire hazards.